The Most Hated Question In Security
After taking an informal and unscientific poll, the most hated security question is, “Are we secure?” Only slightly better is, “Are we secure against known threats?” It’s rarely asked the second way. Both are dreaded – particularly in the boardroom.
An altogether better question is, “Are we resilient?” Or said in business terms, “Are we resilient to plausible losses?” That question brings security and finance together. Now united, they must demonstrate that the business is sustainable in the face of losses.
Finance is responsible for dealing with unexpected, yet plausible, financial losses, managed through insurance (risk transfer) and cash reserves (risk acceptance). Security is responsible for reducing the likelihood of plausible losses through risk mitigation. To the detriment of the business, each often works in isolation.
But risk mitigation, transfer, and acceptance should be designed to work together. They are the most collaborative when they have the same objective – keeping risk within tolerance. This should be security’s and finance’s shared north star– they just don’t often recognize it. Financial leaders and security experts must define what risk tolerance is together for the sake of the business.
The Cyber Resilience North Star
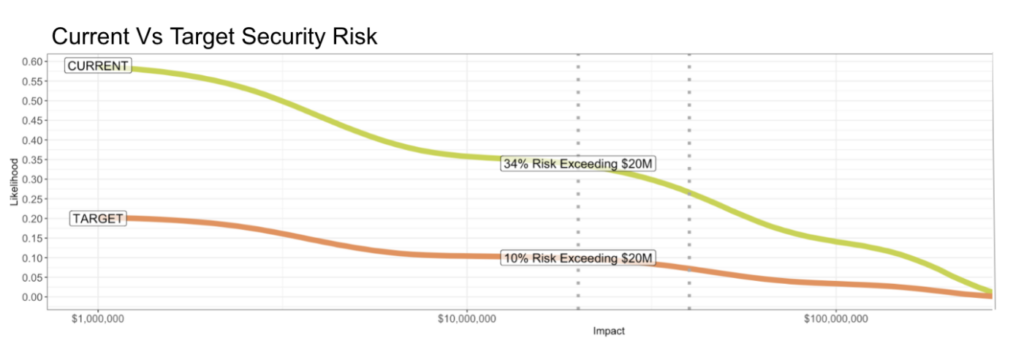
“What’s our risk tolerance?” Most security leaders hate this question too. Some might say it’s worse than “Are we secure?” Yet you may be surprised to learn that the business already answers this question (in part) when they buy cyber insurance. What they are buying is a limit. A limit is a key piece of the risk tolerance puzzle. Your CFO wants a limit large enough to keep people’s mitts off their capital reserves – within reason.
- Risk of Exceeding Insurance Limit $20M: 34% Risk of Exceedance
Whether your CFO frames it this way or not, they are saying, “Any impacts beyond our limit will be handled by our cash reserves – our treasury – and we can only take so much of that.” Currently, this is said in isolation to security.
Most likely, they would prefer to say the following, “Our investments in security and insurance combined with our cash reserves (as a backstop) make us resilient to plausible cyber losses. Our strategy does this without incurring the moral hazards of under-investment nor the excesses of fear, uncertainty, and doubt.”
What the CFO is saying, in a qualitative manner, is that risk is being managed to tolerance.
Framing The Tolerance Question Quantitatively
“Are you okay with a 34% chance of losing $20 million or more – over the next three years?” Better still, “Are you okay with a 34% chance of losing $20 million with a 20% chance of losing $100 million or more – over the next three years?”
What’s wrong with this last question? There is a problem. A big one. A brave soul will invariably say, “It’s relative…risk is relative!” But what we must be asking is, “Relative to what specifically?”
Risk is relative to the cash you have on hand. If your reserves are in the billions, then these losses may not be the first thing you think about when waking up. You may be tolerant of these potential losses. However, many companies would find these losses concerning – particularly given the extent of the tail risk.
Tolerance Is Found Through Scenario Modeling
Here’s a thought-provoking question: As stated, over a three-year period, you face a 34% chance of losing $20 Million and a 20% chance of losing $100 Million or more. What might you be willing to pay each year (over three years) to move that to a 10% chance of losing $20M and a 5% chance of losing $100M or more? Note: you may want to read that twice and look at the first graph above.
This type of question cannot be answered by any form of benchmarking. It can only be answered by running numerous strategic scenarios that consider:
- The cost of a desired insurance limit
- The cost (and return on) security controls
- The magnitude and probability of losses potentially impacting reserves
Those scenarios will reflect your company’s value at risk (exposure) and your company’s financial position as it evolves. You and your CFO (at the very least) need to see the potential impacts of different strategy scenarios as a team. Facing these quantitatively, you will recognize risk and cost trade-offs that must be considered before committing to an integrated risk management strategy. Taken together, all of this informs what your tolerance is and how much you should spend to keep risk within it.
Does building resilient strategies that aim to keep risk within tolerance sound important to you? Learn more by signing up for our community webinars or onsite training. For a collaborative and quantitative risk management engagement with our experts, contact us directly at cyber-risk-quant@resilienceinsurance.com
*Please note: All percentages, risk calculations, and models in this article are for illustrative purposes only.







